Neuroradiology
What is Neuroradiology?
Neuroradiology is a subspecialty of radiology that focuses on:
- Diagnosis of injuries, diseases, and disorders of the central nervous system or peripheral nervous system
- Minimally invasive treatment for brain or spinal cord injuries, diseases, or disorders
Neuroradiologists are highly trained physicians who work closely with neurologists and neurosurgeons to provide and interpret imaging that provides accurate diagnosis and minimally invasive treatments of injuries, diseases, and disorders of the central nervous system or peripheral nervous system.
Neuroradiologists interpret x-rays, magnetic resonance images (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scans of the brain, spine and spinal cord, face and neck, and peripheral nerves. They also perform angiographic studies of the brain and spine and interpret the findings.
The following list provides an overview of diagnostic and therapeutic techniques used by neuroradiologists:
- Diagnostic MRI methods, including:
- MRI
- MR spectroscopy (MRS)
- Functional MRI (fMRI)
- MR angiography (MRA)
- Perfusion and diffusion techniques
- Contrast-enhanced techniques
- CT methods
- CT angiography (CTA)
- Perfusion techniques
- Contrast-enhanced techniques
- Catheter angiography
- Embolization
- Coil placement
- Stent placement
At Barrow, neuroradiologists:
- Provide excellent patient care
- Train the next generation of neuroradiologists
- Perform research that will shape clinical practice and improve the lives of patients
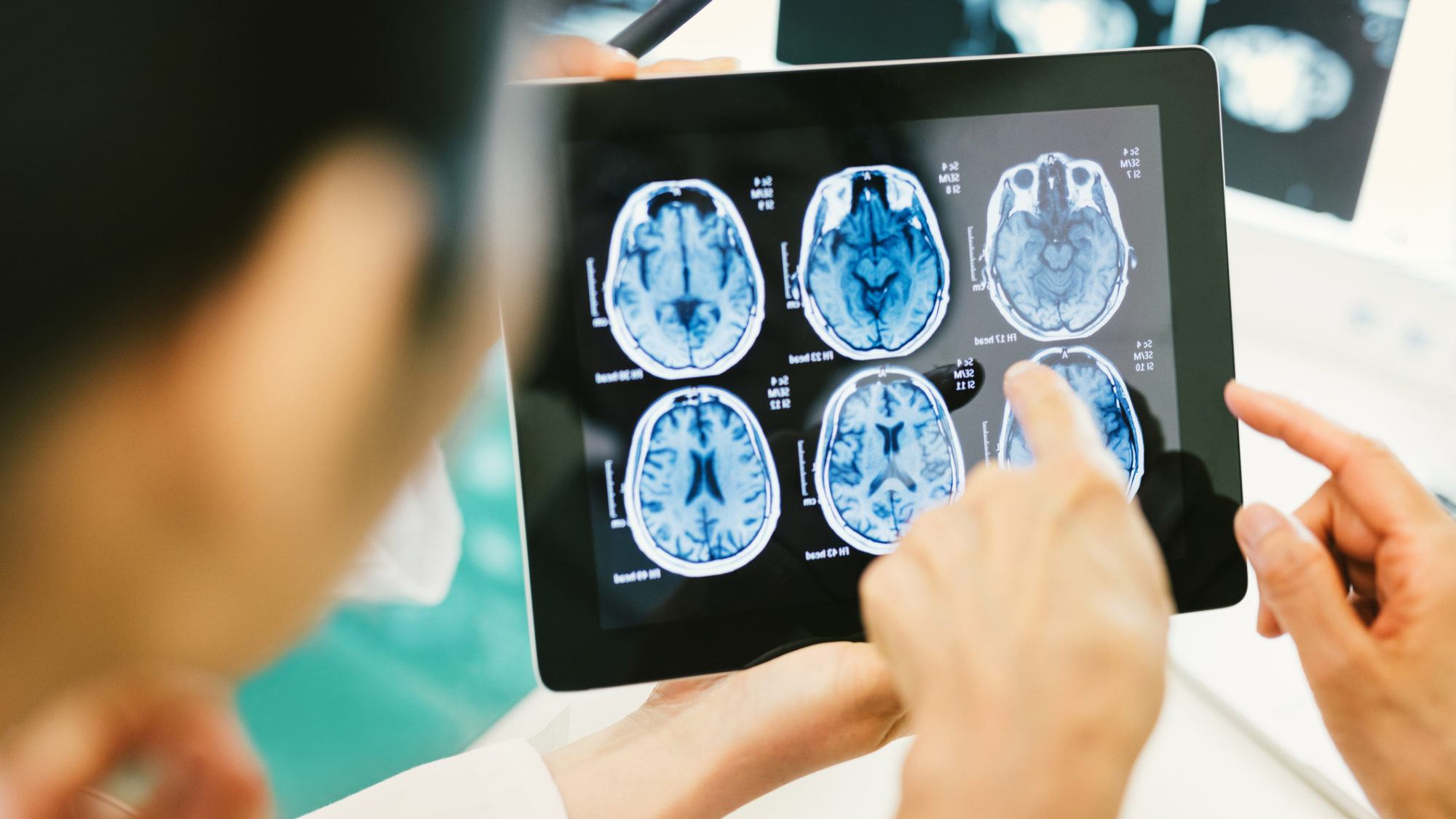
What is Neuroradiology used for?
Neuroradiology is primarily used to diagnose brain or spinal cord injuries, diseases, or conditions, such as:
- Blood vessel disorders in the brain or spinal cord, such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVM), and dural arteriovenous fistulae
- Brain injury, including anoxic injury or traumatic brain injury
- Brain tumors, both benign and cancerous
- Degenerative disorders (disorders that get worse over time) such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington’s chorea, and Alzheimer’s disease
- Functional disorders, such as headache, seizure disorder, dizziness, balance disorders, and neuralgia
- Infections, such as meningitis, encephalitis, polio, and brain abscesses
- Movement disorders, such as dyskinesia and essential tremor
- Neuromuscular disorders, such as Bell’s palsy, cervical spondylosis, peripheral neuropathy, muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Stroke disorders such as ischemic strokes (caused by blood clots), hemorrhagic strokes (caused by bleeding in the brain), and transient ischemic attacks (TIA or “mini-stroke”)
Although neuroradiology is primarily a diagnostic service, neuroradiologists may also perform or assist with some minimally invasive treatments for neurological disorders, such as brain aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVM), and compression fractures of the spine.
Am I a good candidate for Neuroradiology?
As mentioned above, neuroradiology is most commonly used to diagnose neurological diseases and injuries to the nervous system. The status of your injury, disease, or condition will help you and your neurologist or neurosurgeon make decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment.
A neuroradiologist may also be able to provide you some minimally invasive options for treatment for certain disorders of the brain and spinal cord.



